Integumentary
System
System
The integumentary system consists of the skin and its annexes. The skin or integument is the body that forms the boundary of the body, lining its outer surface and the first protective barrier of the body.
The skin is a clear example of how different fabrics work together to provide a body of functions that would otherwise not be possible to fulfill.
To perform their specialized functions, the skin has basic requirements that must be met by different tissues. It should be waterproof, this character is what gives its epithelium. Required mechanical strength, provided by a fabric support of the extracellular matrix secreted by fibroblasts. You need the blood supply to the transport of substances, these are exchanged across the endothelium (epithelial tissue) blood vessels. Blood vessels are also the path of immune cells to the skin. Nerve fibers are necessary to transmit information to the central nervous system and for distributing signals in the opposite direction, eg to the glands and muscles located in skin.
While protection is the most obvious of all, the skin is responsible for many other functions, thanks to the tissues that form.
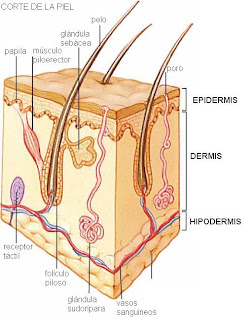
The skin is made of three layers: epithelium, the epidermis, which is the specialized tissue characteristic of this body and its outer part, a tissue, the dermis, below the previous and the hypodermis, the deepest layer.
The skin is a clear example of how different fabrics work together to provide a body of functions that would otherwise not be possible to fulfill.
To perform their specialized functions, the skin has basic requirements that must be met by different tissues. It should be waterproof, this character is what gives its epithelium. Required mechanical strength, provided by a fabric support of the extracellular matrix secreted by fibroblasts. You need the blood supply to the transport of substances, these are exchanged across the endothelium (epithelial tissue) blood vessels. Blood vessels are also the path of immune cells to the skin. Nerve fibers are necessary to transmit information to the central nervous system and for distributing signals in the opposite direction, eg to the glands and muscles located in skin.
While protection is the most obvious of all, the skin is responsible for many other functions, thanks to the tissues that form.
The skin is made of three layers: epithelium, the epidermis, which is the specialized tissue characteristic of this body and its outer part, a tissue, the dermis, below the previous and the hypodermis, the deepest layer.
Epidermis
The epidermis is the tissue of the body most exposed to aggression, must necessarily be adapted for the renovation and repair.
The epidermis is a multilevel epithelium, whose cells are known as keratinocytes, are specialized for the production of keratins, intermediate filament proteins.
The epidermis is a multilevel epithelium, whose cells are known as keratinocytes, are specialized for the production of keratins, intermediate filament proteins.
ennis Back
The dermis is the connective tissue of the skin. It is a loose tissue in its most superficial and denseirregular shaped or not, in its deepest part. Collagen and elastic fibers of the dermis to the skin are resilient and deformable, at the same time.
The dermis is elevations called papillae that project into the epidermis. In some parts of the body, such as palms and soles, the epidermis accompanied folds of the dermis, forming ridges and elevations: these are the tracks that are used to identify people.
The dermis receives abundant blood supply, such as epithelia are vascularized tissues, nutrients and waste must reach the epidermis or to be abandoned, diffuse through the amorphous matrix of the dermis.
The diameter of the blood vessels of the skin is controlled by the autonomic nervous system.Vasodilatation (increase in vessel diameter) and vasoconstriction (diameter reduction) are used to increase or decrease blood flow to the skin. Vasodilatation allows dissipation of body heat into the environment. On the contrary, when it is necessary to conserve heat or derive a greater blood flow to other organs, vasoconstriction occurs.
The dermis is elevations called papillae that project into the epidermis. In some parts of the body, such as palms and soles, the epidermis accompanied folds of the dermis, forming ridges and elevations: these are the tracks that are used to identify people.
The dermis receives abundant blood supply, such as epithelia are vascularized tissues, nutrients and waste must reach the epidermis or to be abandoned, diffuse through the amorphous matrix of the dermis.
The diameter of the blood vessels of the skin is controlled by the autonomic nervous system.Vasodilatation (increase in vessel diameter) and vasoconstriction (diameter reduction) are used to increase or decrease blood flow to the skin. Vasodilatation allows dissipation of body heat into the environment. On the contrary, when it is necessary to conserve heat or derive a greater blood flow to other organs, vasoconstriction occurs.
- Blisters
- Pain (the degree of pain is not related to the severity of the burn -- the most serious burns can be painless)
- Peeling skin
- Red skin
- Shock (watch for pale and clammy skin, weakness, bluish lips and fingernails, and a drop in alertness)
- Swelling
- White or charred skin
Symptoms of an airways burn:
- Charred mouth; burned lips
- Burns on the head, face, or neck
- Wheezing
- Change in voice
- Difficulty breathing; coughing
- Singed nose hairs or eyebrows
- Dark, carbon-stained mucus
ULCERS:
Most ulcers are caused by infection, not spicy or highly seasoned, either by acid or emotional stress.
- The most common symptom of ulcers is heartburn.
- Your doctor can test for the bacteria H. pylori.
- Antibiotics are the new way to cure ulcers.
- Being able to eliminate the infection caused by H. pylori with antibiotics means that ulcers can be cured permanently.
If you think you suffer from an ulcer, if they have already been diagnosed or has had to live with an ulcer for years, this booklet brings good news.Recently, scientists discovered that most ulcers are caused by an infection.Following appropriate treatment, the ulcer - and the pain it causes - may disappear forever.
Twenty-five million people in the U.S. suffer from ulcers. An ulcer is a lesion or hole in the lining of the stomach or duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). Ulcers can affect both women and men regardless of age.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is the name of a bacterium that lives in the lining of the stomach. Although previously thought to spicy food or spicy, acid and stress were the major causes of ulcers, we now know that nine out of ten ulcers are caused by the bacterium H. pylori. Drugs that reduce stomach acid can help the person feel better, but the pain may recur. Now the good news: since many of ulcers are caused by this bacterial infection can be cured permanently with the help of appropriate antibiotics.
What are the symptoms of ulcers?
- The most common symptom of an ulcer is pain or burning in the abdomen between the breastbone and the navel. Usually the pain occurs either when the stomach is empty, between meals or early in the morning, but can occur at any time of day. The pain can last a few minutes to hours and is usually relieved by eating something or taking antacids.
- Less common symptoms are nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite.
- Sometimes the ulcers can bleed, if the bleeding or bleeding continues for an extended period can cause anemia that causes weakness and fatigue.
- If the bleeding is heavy, you may see blood in vomit or stool. Feces containing blood may be dark red or black.
An allergy is a reaction of your immune system to something that does not bother most other people. People who have allergies often are sensitive to more than one thing. Substances that often cause reactions are
- Pollen
- Dust mites
- Mold spores
- Pet dander
- Food
- Insect stings
- Medicines
How do you get allergies? Scientists think both genes and the environment have something to do with it. Normally, your immune system fights germs. It is your body's defense system. In most allergic reactions, however, it is responding to a false alarm.
Allergies can cause a runny nose, sneezing, itching, rashes, swelling or asthma. Symptoms vary. Although allergies can make you feel bad, they usually won't kill you. However, a severe reaction called anaphylaxis is life-threatening.
Viral infections
Viral diseases are the group most common infectious diseases in childhood, and its very common skin symptoms. It should also be remembered that in the first years of life there is a special predisposition to these infections in relation to the immunological immaturity of both humoral and cellular. Skin lesions can be caused by the virus itself, which may be isolated or, conversely, the clinical skin is the result of interaction with the immune system, as in the case of most rash diseases. We should note also that the lesions are nodular or vesicular which may contain the virus and potentially infectious.
- Fungal skin infections are infections of the skin caused by dermatophytes and yeasts, which are groups of fungi that are normally harmless. When these grow excessively, they can cause the symptoms of a fungal skin infectionfungal infections are infections caused by a fungus, a type of microorganism. Two common causes of fungal infections are a fungus called tinea and yeast infections caused by the fungus Candida albicans.Some very common types of fungal infections caused by tinea include:
- Athlete's foot
- Jock itch
- RingwormCommon yeast infections, also called candida and candidiasis, can infect other areas of the body including:
- Digestive tract (gastroenteritis)
- Lungs
- Mouth (oral thrush)
- Vagina (vaginal yeast infection, vaginal thrush)
- In most cases, fungal infections are treatable in generally healthy people. However, these infections are more likely to occur and can be more difficult to treat in people with weakened immune systems due to such conditions as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or taking steroid medications or chemotherapy. In these cases, complications of fungal infections may become life threatening.
Recurring fungal infections can also be a symptom of a serious, undiagnosed, underlying disease, such as HIV/AIDS or diabetes. Seek prompt medical care for recurring fungal infections including vaginal yeast infections.
Symptoms of fungal infections differ depending on the type and severity of the infection, the area of the body affected, and individual factors.Symptoms of athlete's foot
Symptoms of athlete's foot include: - Itching of the feet
- Scaling and flaking of the skin of the feet
- Thick, yellowish toenails that detach from the nail beds if the fungus infects the toenails
Symptoms of jock itch
Symptoms of jock itch most often occur in men and include: - Itching of the groin area
- Red, scaly rash in the groin area
Symptoms of ringworm
Symptoms of ringworm include: - Red, itchy area on the scalp, often in the shape of a ring
- Hair loss in the affected area
Symptoms of fungal infections that affect the mouth
Symptoms of fungal infections that affect the mouth (oral thrush) include: - Lesions or sores that are raised, are yellow-white in color, and appear in patches in the mouth or throat and/or on the tongue
- Sore, bleeding gums
- Patches or lesions that become sore, raw and painful, making it difficult to eat or swallow
Symptoms of fungal infections that affect the vagina
Symptoms of fungal infections that affect the vagina (vaginal thrush) include: - Thick, white vaginal discharge that has a texture similar to cottage cheese
- Vaginal irritation
- Vaginal itching
- Burning with urination
Symptoms of fungal infections that affect the digestive tract
Symptoms of fungal infections that affect the digestive tract (fungal gastroenteritis) include: - Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Recurrent fungal infections can be a symptom of a more serious condition, such as HIV/AIDS or diabetes. It is important to seek prompt medical care for repeated fungal infections, such as repeated vaginal yeast infections or oral thrush.What causes fungal infections?
Different types of fungus cause a variety of fungal infections: - Athlete's foot, jock itch, and ringworm are caused by a fungus called tinea.
- Most yeast infections, such as vaginal thrush, oral thrush, and fungal gastroenteritis, are caused by a fungus called Candida albicans. Fungus can also cause fungal infections of the lungs due to inhaled fungal spores.Certain factors or conditions can result in an overgrowth of fungus in the body. These include:
- Taking antibiotics. Antibiotics can kill off "healthy" bacteria in the body, as well as bacteria that cause disease. When antibiotics kill the healthy bacteria, the normal balance of microorganisms in the mouth, vagina, intestines, and other places in the body is altered, resulting in an overgrowth ofCandida albicans or other fungi.
- Having a weakened immune system due to certain conditions, such as HIV/AIDS or taking steroid medications or chemotherapy
- Having high blood sugar due to diabetes, which provides food for Candida albicans and encourages its overgrowthFungal infections can also be passed from a pregnant woman to her infant during vaginal delivery or breastfeeding.
What are the risk factors for fungal infections?
A number of factors increase the risk of developing fungal infections. Not all people with risk factors will develop fungal infections. These factors include: - Being very young or very old
- Douching or using feminine deodorants or scented tampons
- Having diabetes
- Having a weakened immune system due to such conditions as HIV/AIDS, or taking steroid medications or chemotherapy
- Taking strong antibiotics, especially for long periods of time
- Wearing tight-fitting underwear, thongs, jeans, or other pants if you are a female
Reducing your risk of fungal infections
You can lower your risk of developing or transmitting fungal infections by: - Avoiding douching
- Cleansing the genitals daily with mild soap and water
- Eating a well-balanced, healthy diet
- Following your treatment plan for conditions, such as diabetes and HIV/AIDS
- Getting early and regular prenatal care when pregnant
- Not using feminine deodorants or scented or deodorant tampons
- Not wearing tight-fitting underwear, thongs, jeans, or other pants if you are a female
- Nursing women who have nipple discharge or pain should notify their provider so they can be examined for fungal infections of the nipples, which could be transmitted to the mouth of a nursing infant.
- Changing tampons frequently
- Seeking regular routine medical care
- Taking antibiotics only when prescribed by your health care professional and finishing the medication exactly as directed
- Wearing cotton underwear
BACTERIAL INFECTION:Bacteria are living things that have only one cell. Under a microscope, they look like balls, rods or spirals. They are so small that a line of 1,000 could fit across a pencil eraser. Most bacteria won't hurt you - less than 1 percent makes people sick. Many are helpful. Some bacteria help to digest food, destroy disease-causing cells and give the body needed vitamins. Bacteria are also used in making healthy foods like yogurt and cheese.But infectious bacteria can make you ill. They reproduce quickly in your body. Many give off chemicals called toxins, which can damage tissue and make you sick. Examples of bacteria that cause infections include Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and E. coli.Antibiotics are the usual treatment. When you take antibiotics, follow the directions carefully. Each time you take antibiotics, you increase the chances that bacteria in your body will learn to resist them. Later, you could get or spread an infection that those antibiotics cannot cure.Parasites are living things that use other living things - like your body - for food and a place to live. You can get them from contaminated food or water, a bug bite, or sexual contact. Parasitic diseases can cause mild discomfort or be deadly.Parasites range in size from tiny, one-celled organisms called protozoa to worms that can be seen with the naked eye. Some parasitic diseases happen in the United States. Contaminated water supplies can lead to Giardia infections. Cats can transmit toxoplasmosis, which is dangerous for pregnant women. Others, likemalaria, are common in other parts of the world.If you are traveling, it's important to drink only water you know is safe. Prevention is especially important. There are no vaccines for parasitic diseases. Some medicines are available to treat parasitic infections.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario